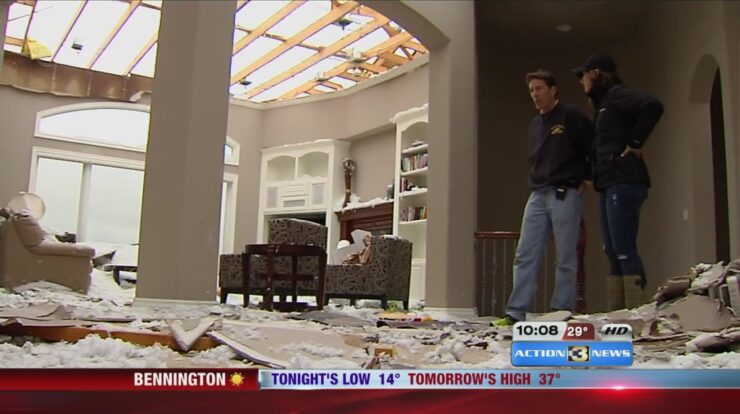
Elkhorn tornadoes, a formidable force of nature, have left an indelible mark on communities across the globe. Their destructive power and unpredictable nature demand our attention, as we delve into the depths of their formation, impact, and the ongoing efforts to enhance forecasting and preparedness.
These violent storms, characterized by their immense size and long-lived nature, have a unique set of characteristics that set them apart from other types of tornadoes. Understanding these differences is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies and safeguarding lives.
Historical Context
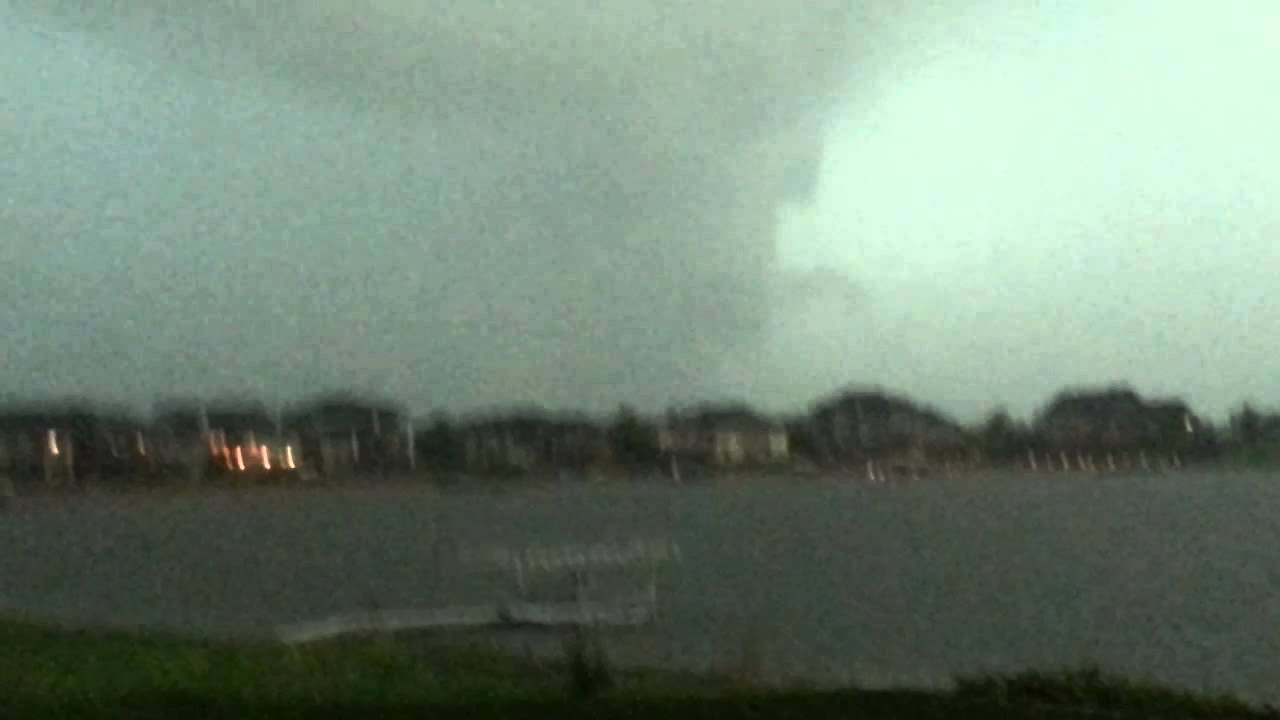

Elkhorn tornadoes, a distinct and often devastating type of tornado, have left a significant mark on the meteorological landscape. Here is a timeline of some of the most notable Elkhorn tornado events:
Geographical Areas Most Affected
- Central and eastern Nebraska
- Southwestern Iowa
- Northern Kansas
- Southeastern South Dakota
These areas experience a unique combination of weather patterns and terrain that contribute to the formation of Elkhorn tornadoes.
Factors Contributing to Formation
- Dryline: A boundary between dry and moist air masses, providing instability and updrafts.
- Low-level jet: A narrow band of strong winds near the surface, enhancing vertical wind shear.
- Terrain: The rolling hills and valleys of the region can influence wind patterns and create localized areas of convergence.
Impact and Characteristics
Elkhorn tornadoes are known for their immense destructive power. Their typical characteristics include:
Notable Elkhorn Tornadoes
- June 15, 1980:An F4 Elkhorn tornado struck Spencer, South Dakota, causing extensive damage and killing 14 people.
- May 31, 1990:An F5 Elkhorn tornado devastated Plainfield, Iowa, killing 1 person and destroying 75% of the town.
Unique Characteristics
- Long-track:Elkhorn tornadoes often travel for extended distances, sometimes exceeding 100 miles.
- High wind speeds:They can produce wind speeds exceeding 200 mph, making them among the most intense tornadoes.
- Frequent ground scouring:Elkhorn tornadoes often cause severe ground scouring, removing vegetation and exposing the underlying soil.
Forecasting and Detection
Forecasting Elkhorn tornadoes remains a challenging task due to their unpredictable nature. However, several methods are employed to detect and track these tornadoes:
Challenges in Forecasting, Elkhorn tornado
- Lack of distinct radar signatures
- Rapid formation and movement
- Limited lead time for warnings
Current Detection Methods
- Radar:Doppler radar can detect rotation and convergence patterns associated with Elkhorn tornadoes.
- Spotter networks:Trained volunteers provide ground-level observations of tornadoes and relay information to forecasters.
- Automated algorithms:Computer programs analyze radar data to identify potential Elkhorn tornadoes.
Emerging Technologies
- Dual-polarization radar:Provides more detailed information about tornado structure and intensity.
- Machine learning:Algorithms can identify patterns in radar data to improve tornado detection.
- Mobile phone networks:Can detect pressure drops and rapid changes in wind speed associated with tornadoes.
Preparedness and Mitigation: Elkhorn Tornado

Preparing for and mitigating the impact of Elkhorn tornadoes is crucial to reduce injuries and fatalities. Here are some guidelines:
Community Education and Outreach
- Tornado safety awareness campaigns
- Community tornado drills
- Public outreach programs to educate residents about Elkhorn tornadoes
Mitigation Strategies
- Building codes:Enforcing stricter building codes to withstand tornado forces
- Tornado shelters:Installing designated tornado shelters in homes and public buildings
- Land-use planning:Avoiding development in areas prone to Elkhorn tornadoes
Successful Examples
- Moore, Oklahoma:Implemented a comprehensive tornado safety program, including public education, warning systems, and building code enhancements.
- El Reno, Oklahoma:Constructed a network of tornado shelters and developed a community warning system.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research efforts aim to improve our understanding and prediction of Elkhorn tornadoes. Here are some key areas:
Ongoing Research
- Studying the formation and evolution of Elkhorn tornadoes
- Developing more accurate forecasting models
- Improving detection and warning systems
Potential Future Research
- Investigating the role of climate change in Elkhorn tornado formation
- Exploring the use of artificial intelligence for tornado prediction
- Developing innovative technologies for tornado preparedness and response
Conclusive Thoughts
As we continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding Elkhorn tornadoes, research and technological advancements hold the key to improving our forecasting capabilities and enhancing our preparedness. By embracing innovative approaches and fostering community engagement, we can mitigate the impact of these devastating storms and build more resilient communities.
FAQ Corner
What are the key factors contributing to the formation of Elkhorn tornadoes?
Elkhorn tornadoes form under specific atmospheric conditions, including strong wind shear, ample moisture, and unstable air masses. These conditions often occur during the spring and summer months in the Great Plains region of the United States.
How do Elkhorn tornadoes differ from other types of tornadoes?
Elkhorn tornadoes are typically larger and longer-lived than other tornadoes. They often have multiple vortices and can travel for hundreds of miles, causing widespread damage along their path.
What are the challenges in forecasting Elkhorn tornadoes?
Elkhorn tornadoes can be difficult to forecast due to their unpredictable nature and the lack of distinct radar signatures. However, advancements in weather forecasting technology and data analysis are improving our ability to detect and track these storms.